This worksheet introduces students to the skeletal system, focusing on bone structure, joints, and their functions․ It includes labeling exercises, multiple-choice questions, and interactive activities to enhance learning․

Overview of the Skeletal System
The skeletal system consists of 206 bones, joints, cartilage, and ligaments, forming the body’s framework․ It provides structural support, protects internal organs, and aids in movement․ Bones vary in shape and size, categorized as long, short, flat, or irregular․ The system also produces blood cells in bone marrow․ Understanding the skeletal system is essential for grasping human anatomy and health․ This worksheet offers a comprehensive review, including labeling diagrams and answering questions to reinforce knowledge of bones, joints, and their functions;
Importance of the Worksheet for Learning
This worksheet is a valuable educational tool for understanding the skeletal system․ It engages students through labeling exercises, multiple-choice questions, and interactive activities, making complex concepts accessible․ By focusing on bone structure, joints, and functions, it reinforces foundational knowledge․ The worksheet caters to different learning styles, encouraging visual and hands-on learners to participate․ Its clear format and comprehensive content make it ideal for classroom use or self-study․ Regular practice with such materials enhances retention and prepares students for further anatomy studies․ It is also available for free online, making it a convenient resource for educators and students alike․

Functions of the Skeletal System
The skeletal system supports the body, protects internal organs, facilitates movement, and produces blood cells․ It is essential for maintaining posture, enabling mobility, and overall bodily function․
Support and Shape of the Body
The skeletal system provides structural support, acting as a framework for the body․ Bones work as levers, enabling movement and maintaining posture․ They distribute weight evenly and protect soft tissues․ The arrangement of bones gives the body its shape, while cartilage and ligaments offer flexibility․ This system supports internal organs, ensuring proper bodily functions․ Understanding bone structure through worksheets helps students visualize how bones contribute to overall body stability and form, making it a crucial part of anatomy education․
Protection of Internal Organs
The skeletal system plays a vital role in safeguarding vital organs․ The skull protects the brain, while the ribcage shields the heart, lungs, and liver․ Vertebrae guard the spinal cord, ensuring nerve function remains intact․ These protective mechanisms are essential for survival, preventing damage from external forces․ Worksheets often highlight this function, helping students understand how bones act as a defensive barrier․ Such exercises emphasize the skeletal system’s critical role in maintaining internal organ safety and overall bodily integrity through structured learning activities․
Movement and Muscle Attachment
Bones serve as anchors for muscles, enabling movement through muscle contraction and relaxation․ The skeletal system acts as a system of levers, allowing muscles to pull on bones and facilitate motion․ This partnership between bones and muscles enables a wide range of movements, from walking and running to fine motor skills․ Worksheets often include exercises that highlight how muscles attach to bones via tendons, creating a functional system for movement․ This interaction is crucial for locomotion and maintaining posture, making it a key focus in skeletal system studies․
Blood Cell Production
Bones play a vital role in blood cell production through bone marrow, the spongy tissue inside certain bones․ Bone marrow produces stem cells, which develop into red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets․ Red blood cells carry oxygen, white blood cells fight infections, and platelets aid in blood clotting․ This process, called hematopoiesis, is essential for maintaining healthy blood and immune function․ Worksheets often highlight this function, emphasizing the skeletal system’s role in supporting life-sustaining processes beyond structural support and movement․

Structure of Bones
Bones are composed of bone tissue, which includes compact bone and spongy bone․ They consist of cells like osteoblasts and osteoclasts, providing structural support and muscle attachment points․
Definition and Components of Bones
Bones are rigid, calcified organs that form the framework of the body․ They consist of bone tissue, which is made up of cells like osteoblasts and osteoclasts, and a matrix of collagen and minerals․ The bone marrow inside bones produces blood cells, while the periosteum, a protective layer, covers the outer surface․ Bones also feature an epiphyseal plate, responsible for growth in length, and are categorized into types like long, short, and flat based on their shapes and functions․ Understanding these components is essential for studying the skeletal system․

Types of Bones (Long, Short, Flat, Irregular)
Bones are classified into four main types based on their shapes and functions․ Long bones, like the femur and humerus, are longer than they are wide and support body movement․ Short bones, such as the carpals and tarsals, are cube-shaped and provide stability․ Flat bones, including the skull and ribs, are broad and protect internal organs․ Irregular bones, like vertebrae, have unique shapes that don’t fit other categories․ Understanding these types helps in identifying bones and their roles in the body․
Joints and Their Role
Joints connect bones, enabling movement and providing stability․ They are essential for flexibility and mobility, allowing the skeletal system to function effectively in various physical activities․
Definition and Types of Joints
A joint is a point where two or more bones connect, enabling movement and stability․ Joints are classified into three main types: synovial, cartilaginous, and fibrous․ Synovial joints, like the knee and shoulder, allow significant movement․ Cartilaginous joints, such as those in the spine, provide limited motion․ Fibrous joints, like the skull sutures, are immovable․ Understanding joint types helps in identifying their roles in movement and stability, essential for completing skeletal system worksheets accurately․
Importance of Joints in Movement
Joints are crucial for enabling movement by allowing bones to articulate and flexibility․ They facilitate various movements such as flexion, extension, and rotation, essential for daily activities․ Synovial joints, with their fluid-filled cavities, reduce friction and enhance mobility․ Without joints, the skeletal system would be rigid, making movement impossible․ Understanding their role in movement helps students grasp how the skeletal and muscular systems collaborate, making them a key focus in skeletal system worksheets and educational resources․ This knowledge is vital for comprehending human physiology and biomechanics effectively․

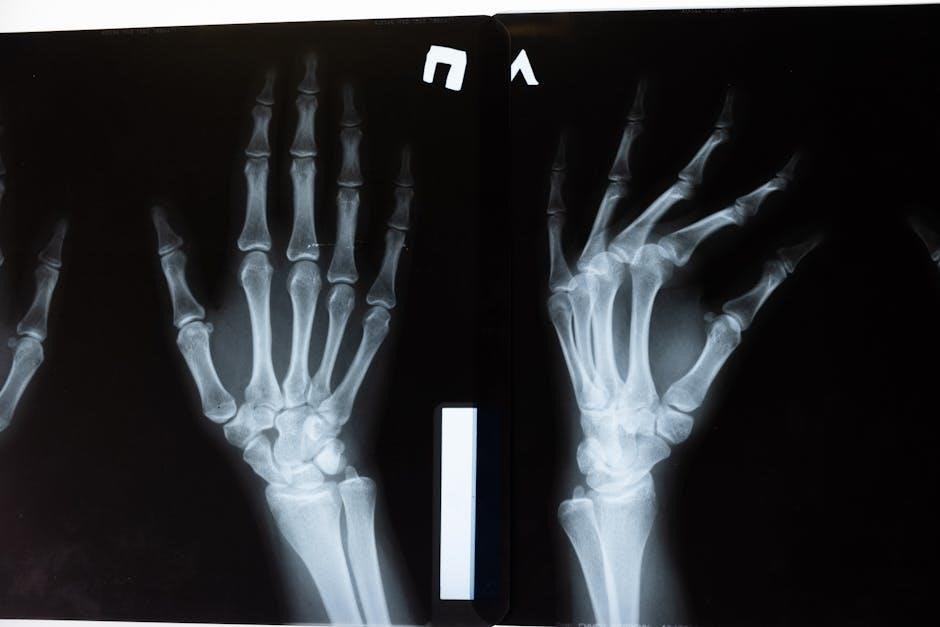
Labeling the Skeleton
Labeling the skeleton helps students identify major bones like the femur, cranium, and ribcage․ Interactive activities, such as diagrams and exercises, make learning engaging and effective for students․
Identifying Major Bones
Identifying major bones is a fundamental skill in understanding the skeletal system․ Worksheets often include diagrams of the human skeleton, allowing students to label bones such as the femur, cranium, and ribcage․ Interactive activities, like matching games and fill-in-the-blank exercises, help reinforce knowledge․ Students learn to recognize the shapes and locations of bones, fostering a deeper appreciation of how the skeletal system supports the body․ These exercises also introduce the concept of bone functions and their roles in movement and protection․
Understanding Bone Marrow and Cartilage
Bone marrow is the spongy tissue inside bones responsible for producing blood cells, including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets․ Cartilage, on the other hand, is a flexible, connective tissue found between bones, acting as a cushion to reduce friction and absorb shock․ Worksheets often include questions about their roles, such as how bone marrow aids in blood production and how cartilage supports joint movement․ These concepts are essential for understanding the skeletal system’s functionality and its role in overall health․
Interactive Learning Activities
Engage with bone labs and hands-on experiments to explore the skeletal system․ Utilize online tools for interactive 3D models and virtual dissections to enhance learning experiences․
bone Lab and Hands-On Experiments
Bone labs offer a hands-on approach to studying the skeletal system, allowing students to explore real or model bones․ Activities include identifying bone types, examining bone marrow, and understanding joint movements․ Interactive experiments, such as creating 3D bone models or simulating fractures, make learning engaging․ These practical exercises help students visualize bone structures and their functions, fostering a deeper understanding of the skeletal system․ Bone labs are an essential tool for making anatomy education interactive and memorable for learners of all ages․

Online Tools for Skeletal System Exploration
Online tools provide interactive and engaging ways to explore the skeletal system․ Websites offer 3D bone models, virtual dissections, and quizzes to test knowledge․ PDF worksheets and interactive diagrams allow students to label bones and joints․ These resources are accessible anytime, making them ideal for homework or self-study․ They enhance learning by providing visual and hands-on experiences, helping students better understand bone structures and functions in an engaging and accessible manner․

Safety and Injury Prevention
Preventing bone fractures and injuries is crucial․ Common fractures include breaks in arms, legs, and hips․ Proper nutrition, exercise, and safety measures strengthen bones and reduce risks․
Common Bone Fractures and Prevention
Common bone fractures often occur in the arms, legs, hips, and collarbone, typically due to accidents, falls, or sports injuries․ Proper nutrition and regular exercise strengthen bones, reducing fracture risks․ A balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D supports bone health․ Wearing protective gear during physical activities and ensuring safe environments can prevent injuries․ Understanding fracture prevention is essential for maintaining skeletal health and avoiding costly treatments․ Regular check-ups and bone density tests are recommended, especially for high-risk individuals․ Safe practices promote long-term skeletal well-being and independence․
Practices to Strengthen Bones
Regular exercise, such as weight-bearing activities like walking or jogging, helps strengthen bones․ A balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D is essential for bone health․ Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption also supports bone strength․ Incorporating resistance training, like lifting weights, can improve bone density․ Staying hydrated and maintaining a healthy weight further promotes skeletal health․ Engaging in these practices reduces the risk of fractures and osteoporosis, fostering long-term bone strength and overall well-being for individuals of all ages․
This worksheet provides a comprehensive overview of the skeletal system, emphasizing bone functions, structure, and joints․ Interactive exercises and bone health practices encourage further exploration and understanding of skeletal anatomy․
The skeletal system comprises 206 bones, providing support, protection, and aiding movement․ Bones contain marrow and cartilage, while joints enable flexibility․ Worksheets cover bone types, functions, and injury prevention, enhancing understanding of skeletal anatomy through interactive exercises and labeling activities․ This educational tool promotes comprehension of bone health and structure, encouraging further exploration of the human body’s framework․ It serves as a foundational resource for students to grasp essential concepts effectively․
Encouragement for Further Study
Exploring the skeletal system offers a fascinating journey into human anatomy․ Students are encouraged to delve deeper by using online tools, watching educational videos, and engaging in hands-on activities․ Understanding bones and joints can inspire careers in medicine, biology, or sports science․ Encourage learners to explore real-world applications, such as osteology or orthopedics, to broaden their knowledge․ Continuous study fosters a deeper appreciation for the body’s structure and function, opening doors to exciting discoveries in health and science․
